Allelopathic Effects of Aqueous Extracts From Sesame Leaves and Root on the Germination and Seedlings Growth of Maize and Sorghum
Keywords:
Allelopathic, Aqueous, Sesame, Leaves, Root, Germination, Seedlings, Growth, Maize, SorghumAbstract
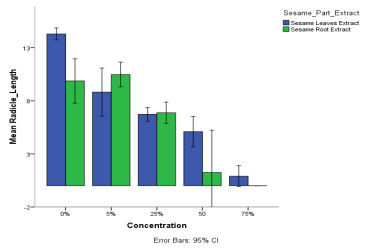
A laboratory and screen house experiment was carried out to investigate the allelopathic impacts of sesame (Sesamum indicum) leaf and root extracts at concentrations of 0%, 5%, 25%, 50%, and 75% on the germination, root and shoot development, seedling growth, plant height, leaf count, fresh and dry weight, germination rate, germination percentage, and photosynthetically active radiation in maize and sorghum seedlings. The findings revealed that the highest germination rates occurred at 5% and 25% concentrations, as well as in the control plants, showing statistically significant differences at (P<0.05). Conversely, germination was reduced at 50% concentration and completely inhibited at 75% concentration in root extract treatments. Measurements of plumule and radicle length, along with fresh and dry weights, demonstrated notable differences in maize when compared to sorghum. Moreover, root growth exhibited greater sensitivity to the allelopathic effects than shoot growth, a pattern similarly reflected in plant height and leaf numbers. The vigor index, germination rate index, and germination percentage were highest in the 5%, 25%, and control treatments for both maize and sorghum, while these parameters were lowest at 50% and 75% concentrations. These results indicate that lower concentrations of leaf or root extracts exert minimal effects on germination and seedling development in both maize and sorghum, with the intensity of the impact being concentration-dependent.
References
Dhanu U., Sheeja K. R, Shalini P.R., Ameena1, M., Jacob, D. and Atul J. “Stimulatory effect of sesame on the germination and seedling growth of Melochia corchorifolia L”. Indian Journal of Weed Science, Vol. 54, Issue 3, pp. 341–344, 2022.
Alam,S.M, S.A Ala, A.R. Azmi, M.R. Khan and R. Ansari, 2001. “Allelopathy and its role in agriculture”. Online journal of Biological Sciences, Vol. 1, Issue 2, pp. 308-315, 2001.
Dana ED and Domingo F. “Inhibituary effects of aqueous extract of Acacia retinodes Schltdl., Euphorbia serpens L. and Nicotiana glauca Graham on weeds and crops”. Allelopathy journal,Vol. 18, Issue 2, pp. 323-330, 2006.
Tesfay, A. Allelopathic Effect of Aqueous Extracts of Parthenium (Parthenium Hysterophorus L.) Parts on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Maize (Zea Mays L.) Journal of Agriculture and Crops, Vol. 4, Issue 12, pp. 157-163, 2018.
Farooq, M., Jabran, K. Cheema, Z. A., Wahid, A. and Siddique, K.H.M. “Exploiting allelopathy for sustainable agriculture”. Pest Management Science. Vol. 67, Issue 23, pp. 493-506, 2011.
Jabran, K., and Farooq, M. “Implications of potential allelopathic crops in agricultural systems”. In Allelopathy. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. Vol. 2, Issue 5, pp. 349-385, 2013)
Olajire, A. A. and Azeez, L. “Total antioxidant activity, phenolic, flavonoid and ascorbic acid contents of Nigerian vegetables”. African Journal of Food Science and Technology. Vol. 2, Issue 2, pp. 22-29, 2011.
Rice, E. L.. “Allelopathy 2nd Ed.Academia press”, New York, 421p. 1984.
Sheeja K. Raj “Ascorbic acid contents of Nigerian Vegetables”, Journal of weed science, Vol. 54, Issue 3, pp. 341-344, 2022.
ISTA. “International seed Testing Association. International rules for seed testing”. Seed Science and Technology,Vol. 13, Issue 2, pp. 322-326, 1995.
Bhadoria, P. B. S. “Allelopathy: a natural way towards weed management”. American Journal of Experimental Agriculture, Vol. 1, Issue, 3, pp. 7–20, 2011.
Devi, O. I. and Dutta, B. K., “Allelopathic effect of the aqueous extract of parthenium hysterophorus and chromolaena odorata on the seed germination and seedling vigour of zea mays l”. Academic Journal of Plant Sciences, Vol. 5, Issue. 4, pp. 110-113, 2012.
Kruse, M., Strandberg, M and Strandberg, B. “Ecological effects of allelopathic plants”. a review National Environmental Research Institute Suleborg, Denmark, Vol. 6, Issue 10, pp. 234-254, 2000.
Akpan, E. N., Denise, E. M., Ezendiokwelu, E. L., et al.. “Growth response of seedlings of Zea mays (L.) to aqueous extract of Lycopodium clavatum (L.)”. MOJ Biol Med. Vol. 2, Issue 4, pp. 287?289, 2017.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.






