SNP Variety of UMOD Gene in Patients with Hypertension Disease in Hilla Province
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26438/ijsrbs.v12i2.681Keywords:
Hypertension, Umod, Gene Polymorphisms, SSCP, PCRAbstract
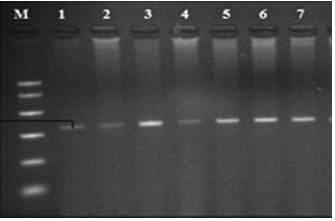
A major risk factor for cardiovascular illnesses, hypertension—also known as high blood pressure—is shaped by both environmental and hereditary elements. Recent research have shown several genetic variations linked to hypertension, among which the rs13333226 variant found in the Uromodulin gene (UMOD). This paper explores the biological relevance of Uromodulin, consequences of the rs13333226 variation, and possible function in hypertension. Fifty blood samples in all came from diabetic patients visiting the Diabetes Center at Merjan Teaching Hospital in Babylon, Iraq. Five samples in all were also gathered to act as a control group. PCR magnificues DNA taken from blood samples. The SOD2 gene was genotyped using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method then applying the DNA single-stranded conformation polymorphism (SSCP) method. The single-stranded conformation polymorphism (SSCP) technique thus verified the genuineness of these DNA polymorphisms. The findings show several haplotypes seen in SOD2. The findings showed that in the sick group the DNA polymorphism distribution was 84% and 16%; in the control group it was 70% and 30%. Understanding hypertension depends much on the rs13333226 variation on the Uromodulin gene. Clarifying the link between this variation and blood pressure control would help scientists open the path for better risk evaluation and focused treatments in the control of hypertension. Complete knowledge of the consequences of this variation and its possible influence in cardiovascular health depends on ongoing research.
References
Natialia Ward, Sara Vickneswaran, and Games Watts, “Lipoprotein (a) and diabetes mellitus: Causes and consequences,” Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 181–187, 2020.
Daehyun Baek et al., “The impact of micrornas on protein output,” Nature, vol. 455, issue. 7209, pp. 64–71, 2008.
Niels Imanningsih, Deddy Muchtadi, Thoms Wresdiyati, and Komari, “Acidic soaking and steam blanching retain anthocyanins and polyphenols in purple Dioscorea alata flour,” Jurnal Teknologi dan Industri Pangan, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 121–128, 2013.
Amanda Crawford et al., “Relationships between single nucleotide polymorphisms of antioxidant enzymes and disease,” Gene, vol. 501, no. 2, pp. 89–103, 2012.
Crowny Wood, “Free radicals in biology and medicine. Third edition Barry Halliwell and John M.C. Gutteridge, Oxford University Press. ISBN 1-29-850044-0/45-0. H/b £75.00, P/b £34.95,” The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, vol. 31, no. 12, p. 1454, 1999.
James Beaudeux et al., “Le stress oxydant, Composante physiopathologique de l’athérosclérose,” Immuno-analyse & Biologie Spécialisée, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 144–150, 2006.
Zahraa Jameel, Zahraa Lawi, Naval Al-Dujaili -Investigation of SOD2 Gene Polymorphism in the Patients with Type Two Diabetes Disease in Babylon Province Biochem Cell Arch, 2019|; vol.10,no.06,pp.70-75
Vaola Palanisamy, Aliex Jakymiw, effef Van Tubergen, Noor D’Silva, and K.aoles Kirkwood, “Control of cytokine mrna expression by RNA-binding proteins and micrornas,” Journal of Dental Research, vol. 91, issue . 7, pp. 651–658, 2012.
Ewa Dudzińska, M. Gryzinska, and J. Kocki, “Single nucleotide polymorphisms in selected genes in inflammatory bowel disease,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2018, pp. 1–5, 2018.
PellaVats, Nera Sagar, Thoms Singh, and Mella Banerjee, “Association ofsuperoxide dismutases(sod1 and SOD2) andglutathione peroxidase 1 (gpx1)gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus,” Free Radical Research, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 17–24, 2014.
Allena Lenzi et al., “Polyunsaturated fatty acids of germ cell membranes, glutathione and blutathione-dependent enzyme-phgpx: From basic to clinic,” Contraception, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 301–304, 2002.
Zahraa Isam Jameel , "Bioinformatics Usage, Application and Challenges to Detect Human Genetic Diseases (Mini Review)," International Journal of Scientific Research in Biological Sciences, Vol.10, Issue.5, pp.59-67, 2023.
Yong Peng and Carlo Croce, “The role of micrornas in human cancer,” Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, vol. 1, issue. 1, 2016.
Chiara Vavassori, Eleonora Cipriani, and Gualtiero Colombo, “Circulating micrornas as novel biomarkers in risk assessment and prognosis of coronary artery disease,” European Cardiology Review, vol. 17, 2022.
Rakesh Pathak and Robert Feil, “Environmental effects on genomic imprinting in development and disease,” Handbook of Nutrition, Diet, and Epigenetics, pp. 3–23, 2019.
Zifeng Wang et al., “Loss of Myc and E-box3 binding contributes to defective Myc-mediated transcriptional suppression of human MC-let-7a-1~let-7d in glioblastoma,” Oncotarget, vol. 7, issue. 35, pp. 56266–56278, 2016.
Ramiro Garzon et al., “MicroRNA-29B induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3b and indirectly DNMT1,” Blood, vol. 113, issue. 25, pp. 6411–6418, 2009.
Dongdong Zeng et al., “DNA tetrahedral nanostructure-based electrochemical MIRNA biosensor for simultaneous detection of multiple mirnas in pancreatic carcinoma,” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, vol. 9, issue. 28, pp. 24118–24125, 2017.
Song Song, Jean Lee, Mean Jeon, Sam Kim, and Sella Sim, “Detection of multiplex exosomal mirnas for clinically accurate diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease using label-free plasmonic biosensor based on DNA-assembled advanced plasmonic architecture,” Biosensors and Bioelectronics, vol. 199, p. 113864, 2022.
Finn Grey et al., “Identification and characterization of human cytomegalovirus-encoded micrornas,” Journal of Virology, vol. 79, issue. 18, pp. 12095–12099, 2005.
Nella Schopman et al., “Deep sequencing of virus-infected cells reveals HIV-encoded small RNAS,” issue of Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 40. 1, pp. 414–427, 2011.
Gerazena Gatto et al., “Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 trans-activates mir-155 transcription through the NF-?B pathway,” Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 36, issue. 20, pp. 6608–6619, 2008.
Rosalind Lee, Rhonda Feinbaum, and Victor Ambros, “The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAS with antisense complementarity to lin-14,” Cell, vol. 75, issue. 5, pp. 843–854, 1993
Qiang. Huang et al., “MicroRNA-21 regulates the invasion and metastasis in cholangiocarcinoma and may be a potential biomarker for cancer prognosis,” Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 829–834, 2013.
Anna Wieckowska et al., “Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis,” The American Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 103, issue. 6, pp. 1372–1379, 2008.
Yong Zhao et al., “Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking MIRNA-1-2,” Cell, vol. 129, issue. 2, pp. 303–317, 2007.
Gerazena Gatto et al., “Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 trans-activates mir-155 transcription through the NF-?B pathway,” Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 36, issue. 20, pp. 6608–6619, 2008.
Sara Linnstaedt, Ellen Gottwein, Rulla Skalsky, Mella Luftig, and Beren Cullen, “Virally induced cellular microRNA Mir-155 plays a key role in B-Cell Immortalization by Epstein-Barr virus," Journal of Virology, vol. 84, issue. 22, pp. 11670–11678, 2010.
Yong Zhao, Evia Samal, and Deran Srivastava, “Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis,” Nature, vol. 436, issue. 7048, pp. 214–220, 2005.
Della VEJRAZKOVA et al., “Distinct response of fat and gastrointestinal tissue to glucose in gestational diabetes mellitus and polycystic ovary syndrome,” Physiological Research, pp. 283–292, 2017.
Ligina Gnudi and Jea Karalliedde, “Beat it early: Putative renoprotective haemodynamic effects of oral hypoglycaemic agents,” Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, vol. 31, no. 7, pp. 1036–1043, 2015.
Mella Brownlee and Allen Cerami, “The biochemistry of the complications of diabetes mellitus,” Annual Review of Biochemistry, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 385–432, 1981.
Heroksa Fukui and Carlos Moraes, “The mitochondrial impairment, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration connection: Reality or just an attractive hypothesis?,” Trends in Neurosciences, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 251–256, 2008.
Jeao McCord and Irwins Fridovich, “Superoxide dismutase,” Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 244, no. 22, pp. 6049–6055, 1969.
Samina Davoudi and Lucia Sobrin, “Novel genetic actors of diabetes-associated microvascular complications: Retinopathy, kidney disease and neuropathy,” The Review of Diabetic Studies, 2016.
Zahraa Isam Jameel, “SNPs variety of 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (HSD3B1) gene are related to prostate cancer in some Iraqi individuals,” Reproduction and Breeding, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 37–43, Jun. 2025.
Zahraa Isam Jameel, “Three FGFR4 gene polymorphisms contribute to the susceptibility of urethral cancer in the middle and south of Iraq population,” Cancer Genetics, vol. 292–293, pp. 77–84, Apr. 2025.
Zahraa Isam Jameel, “Four microrna gene polymorphisms are associated with Iraqi patients with colorectal cancer,” Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, vol. 25, no. 1, Apr. 2024.
Zahraa Isam Jameel , "MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Function, Circulation and Application Role in Human Diseases," International Journal of Scientific Research in Biological Sciences, Vol.10, Issue.5, pp.71-80, 2023.
Zahraa Isam Jameel , "Bioinformatics Usage, Application and Challenges to Detect Human Genetic Diseases (Mini Review)," International Journal of Scientific Research in Biological Sciences, Vol.10, Issue.5, pp.59-67, 2023.
Shymaa. Rabee Banoon et al., “Using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprinting technique to analyze genetic variation in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from different sources in Babylon Province Hospitals,” Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development, vol. 10, no. 9, p. 1300, 2019.
Rakesh Pathak and Robert Feil, “Environmental effects on genomic imprinting in development and disease,” Handbook of Nutrition, Diet, and Epigenetics, pp. 3–23, 2019.
Zifeng Wang et al., “Loss of Myc and E-box3 binding contributes to defective Myc-mediated transcriptional suppression of human MC-let-7a-1~let-7d in glioblastoma,” Oncotarget, vol. 7, issue. 35, pp. 56266–56278, 2016.
Ramiro Garzon et al., “MicroRNA-29B induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3b and indirectly DNMT1,” Blood, vol. 113, issue . 25, pp. 6411–6418, 2009.
Chiara Braconi, Nianyuan Huang, and Tushar Patel, “MicroRNA-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 and tumor suppressor gene expression by interleukin-6 in human malignant cholangiocytes,” Hepatology, 2010.
Ingo Volkmann et al., “MicroRNA-mediated epigenetic silencing of SIRTUIN1 contributes to impaired angiogenic responses,” Circulation Research, vol. 113, issue . 8, pp. 997–1003, 2013.
Baohong Zhang, Xiaoping Pan, George Cobb, and Todd Anderson, “MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors,” Developmental Biology, vol. 302, issue. 1, pp. 1–12, 2007.
Peter Androvic, Sarka Benesova, Eva Rohlova, Mikael Kubista, and Lukas Valihrach, “Small RNA-sequencing for analysis of circulating mirnas,” The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, vol. 24, issue . 4, pp. 386–394, 2022.
Xinna Zhang, Xiongbin Lu, Gabriel Lopez-Berestein, Anil Sood, and George Calin, “In situ hybridization-based detection of micrornas in human diseases,” microRNA Diagnostics and Therapeutics, vol. 1, issue. 1, 2014.
Charles Lawrie et al., “Detection of elevated levels of tumour‐associated micrornas in serum of patients with diffuse large b‐cell lymphoma,” British Journal of Haematology, vol. 141, issue . 5, pp. 672–675, 2008..
Carmen Condrat et al., “MIRNAs as biomarkers in disease: Latest findings regarding their role in diagnosis and prognosis,” Cells, vol. 9, issue. 2, p. 276, 2020.
Dinella Hiam and Servena Lamon, “Circulating micrornas: Let’s not waste the potential,” American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, vol. 319, issue. 2, 2020.
Lewis Hong et al., “Systematic evaluation of multiple qPCR platforms, NanoString and Mirna-Seq for microrna biomarker discovery in human biofluids,” Scientific Reports, vol. 11, issue. 1, 2021.
Shiv Kumar Sharma, Teena Gupta, “A Novel Approach for Plant Environment,” International Journal of Biological Sciences, Vol.4, Issue.12, pp.1-5, 2014.
Reena Solanki, “A Proposed New Approach for Cell Biology,” In the Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference of Medical Sciences, India, pp.542-545, 2016.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to this journal agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, allowing third parties to share their work (copy, distribute, transmit) and to adapt it, under the condition that the authors are given credit and that in the event of reuse or distribution, the terms of this license are made clear.






